C# Tips and Tricks
Reading Outlook Contacts
Have you ever realized all you can do if Outlook contacts information were located into a database? If you have, this tip is for you. The first step is to take all that information out from Outlook so we can transform it into series of insert/update statements.
Start Microsoft Visual C# Express (you can download it for free from Microsoft’s site pending link).
Once downloaded and installed, create a new project and add Outlook’s library to it:
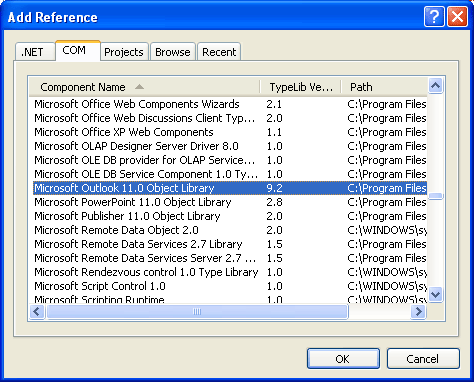
Go to Project -> Add Reference -> COM and select Microsoft Outlook 11.0 Object Library
Add the following line to the beginning of the file:
1using Outlook;
Update:
Last time I did it I had to change last line to this:
1using Outlook = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Outlook;
And here’s the code:
1Outlook.Application app = new ApplicationClass();
2Outlook.NameSpace ns = app.GetNamespace("MAPI");
3ns.Logon("outlook-username", "outlook-password", false, true);
1MAPIFolder apf;
2MAPIFolder contacts;
3string storeId;
1apf = ns.GetDefaultFolder(
2 OlDefaultFolders.olPublicFoldersAllPublicFolders);
3contacts = apf.Folders["your-public-folder-name"];
4
5storeId = contacts.StoreID;
1foreach (Object o in contacts.Items){
2 // Casting is important to avoid any distribution list
3 if (o is ContactItem)
4 {
5 ContactItem c = (ContactItem)o;
6 Console.Writeline(c.LastName + "n");
7 }
8}
9ns.Logoff();
Ok, we now know how to access and loop contacts, the missing thing is how to save them in an external database.
By the way, the ns.Logon function receives four parameters:
- string Profile: that’s your username,
- string Password: that’s your username,
- bool ShowDialog: that’s your username and
- bool NewSession: that’s your username
If the contact list you’re trying to access is not in the root level, but is a subfolder inside a subfolder inside a subfolder… like in the following image:

then this is the way you should go:
1apf = ns.GetDefaultFolder(
2 OlDefaultFolders.olPublicFoldersAllPublicFolders);
3contacts =
4 apf.Folders["International"].Folders["MX"].Folders["Admin Contacts"];
Sending mail from C#
An easy way to send email using C#:
1System.Net.Mail.MailMessage message =
2 new System.Net.Mail.MailMessage();
3message.To.Add("luckyperson@online.microsoft.com");
4message.Subject = "This is the Subject line";
5message.From =
6 new System.Net.Mail.MailAddress("from@online.microsoft.com");
7message.Body = "This is the message body";
8System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient smtp =
9 new System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient("yoursmtphost");
10smtp.Send(message);
source: http://forums.microsoft.com/MSDN/ShowPost.aspx?PostID=717&SiteID=1
System.Transactions
If you want to use System.Transactions in your application,
- Right click project name in Solution Explorer and click Add a Reference…
- In the .NET tab find and select the System.Transactions option
- Click Ok and enjoy.
If you don’t add the reference you will get the following error while compiling:
The type or namespace name ‘Transactions’ does not exist in the namespace ‘System’ (are you missing an assembly reference?)
Creating a message box
Well, it is very simple…
1MessageBox.Show("Your message")
There are many available options… be sure you take a look at them.
Getting the Windows user name, domain, etc…
There are two ways to accomplish this, first the short way:
1Environment.UserName // user
2Environment.UserDomainName // domain
And the long way:
1System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name.ToString();
The long way will give you access to many more options so be sure to explore it.
How to read a text file
Add the following code at the beginning of your file:
1Using System.IO;
And here’s the code…
1String text;
2try {
3 StreamReader sr = new StreamReader("C:file.txt");
4 text = sr.ReadLine();
5 while (text != null) {
6 Console.WriteLine(text);
7 text = sr.ReadLine();
8 }
9 sr.Close();
10 Console.ReadLine();
11}
12catch(Exception ex) {
13 Console.WriteLine("Exception: " + ex.Message);
14}
How to write a text file
Add the following code at the beginning of your file:
1Using System.IO;
And here it goes…
1try {
2 StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter("C:file.txt");
3 sw.WriteLine("Hello World!!!");
4 sw.WriteLine("This is a test");
5 sw.Close();
6}
7catch(Exception e) {
8 Console.WriteLine("Exception: " + e.Message);
9}
How to connect to Access
Code:
1using System.Data.OleDb;
2...
3
4OleDbConnection conn = new OleDbConnection(
5 "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" +
6 "Data Source=C:database.mdb;" +
7 "Jet OLEDB:Database Password=password");
8conn.Open();
9
10OleDbCommand cmd = new OleDbCommand("select * from mytable", conn);
11OleDbDataReader dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
12while (dr.Read())
13{
14 Console.WriteLine(dr.GetString(0));
15}
16conn.Close();
How to connect to MySQL
See my MySQL section.
Error: IErrorInfo.GetDescription Failed with E_FAIL(0x80004005)
When you are querying a database you get this error. The reason is your query is using a keyword for a column name, table, etc. It does not matter if your query works well when you execute it directly in your database manager, remember there are more layers between C# and your database.
Data Types for C# and MSAccess 2002
If you want to do a “perfect” match between data types in MSAccess and C#
C# data types
| C# | CLR | Signed | Memory | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sbyte | System.Sbyte | Yes | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| byte | System.Byte | No | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| short | System.Int16 | Yes | 2 bytes | 32768 to 32767 |
| int | System.Int32 | Yes | 4 bytes | 2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| long | System.Int64 | Yes | 8 bytes | 9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807 |
| ushort | System.Uint16 | No | 2 bytes | 0 to 65535 |
| uint | System.Uint32 | No | 4 bytes | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ulong | System.Uint64 | No | 8 bytes | 0 to 18446744073709551615 |
| float | System.Single | Yes | 4 bytes | 1.5×10-45 to 3.4 x x1038 |
| double | System.Double | Yes | 8 bytes | 5.0×10-324 to 1.7×10308 |
| decimal | System.Decimal | Yes | 12 bytes | 1.0×10-28 to 7.9×1028 |
| char | System.Char | 2 bytes | Unicode characters | |
| boolean | System.Boolean | 1 byte | True or false |
MS Access data types
| MSAccess | Range | Decimal precision | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Byte | 0 to 255 (no fractions) | None | 1 byte |
| Decimal |
10^38-1 through 10^38-1 (.adp) -10^28-1 through 10^28-1 (.mdb) |
28 | 12bytes |
| Integer | -32768 to 32767 (no fractions). | None | 2 bytes |
| Long Integer | (Default) -2147483648 to 2147483647 (no fractions). | None | 4 bytes |
| Single |
-3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 for negative values and 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values. |
7 | 4 bytes |
| Double |
-1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values and 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486231E308 for positive values. |
15 | 8 bytes |
| Replication ID | Globally unique identifier (GUID) | N/A | 16 bytes |
